The Compound That Underground Health And Fitness Geeks Are All Talking About
If you’ve done any digging into the world of health and fitness lately, you’ve likely come across the subject of proteins. Specifically:
- Protein – essential building blocks for health and fitness
- High protein consumption – aids in muscle formation and weight loss
- Protein-rich diets – promoting weight, loss one steak at a time
Thanks to the recent emergence of the keto “kraze,” many people are dabbling in the world of low carbohydrate, high protein, and quality fats, hoping to find those slim, svelte physiques that we’ve all dreamed about for so long. We’ve acquainted ourselves with amino acids and how they function in the body. A condensed list of the benefits of these powerhouse protein compounds includes:
- Facilitating the creation and growth of skin, hair, and muscle tissue
- Producing and protecting neurotransmitters
- Healing and repair of all tissues
- Promoting healthy digestion
- Providing much-needed energy for the body
- Regulating moods and hormones essential for endocrine system function
Those who are self-proclaimed fitness geeks – the ones who really want to get to the bottom of protein synthesis and cellular renewal – are taking their studies a bit further. They’re dipping their toes into the peptide pool…

Peptides: The Next Fitness Sensation?
Recent studies point to peptides as the next “wonder compound,” impacting everything from weight loss and inflammation to the aging process, and it has industry insiders incredibly excited about the implications of these protein building-blocks.
Many people confuse peptides with proteins – and while they’re similar in composition, peptides are known to have fewer amino acids than proteins do. Peptides are available in synthetic supplements and they’re naturally present in some foods; knowing what to eat and how to supplement may be the key to many of our anti-aging woes.
Some of the more popular peptide supplements available on the market today include collagen peptides used for cellular renewal and collagen production, and creatine, which is used for muscle building and improving athletic performance.
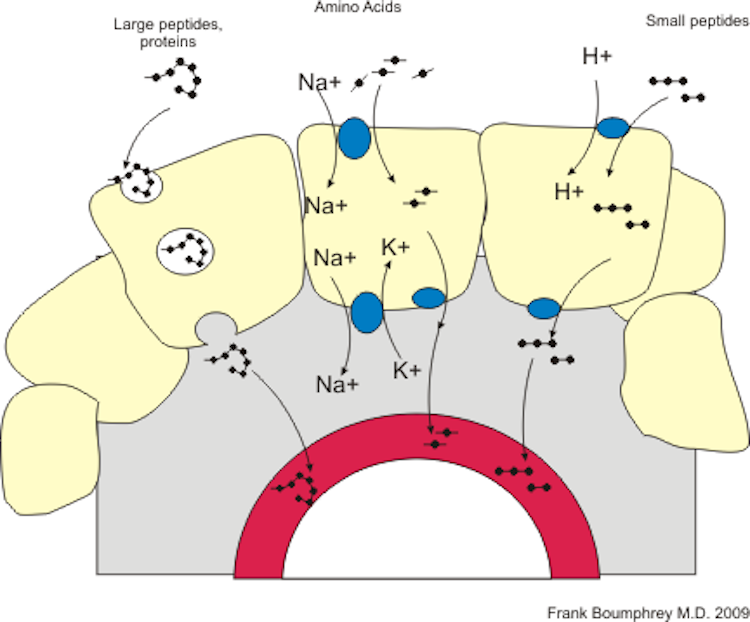
What Are Peptides, Anyway?
Peptides are short strings of amino acids; they’re typically comprised of anywhere from two to 50 amino acids. These shorter chains of amino acids are a bit easier for the body to absorb than proteins. Peptides penetrate the skin and intestines quickly, helping the body to assimilate the beneficial compounds into tissues and cells. Peptides can be found in both plant and animal products, including:
- Eggs
- Milk
- Meat
- Fish and shellfish
- Wheat
- Flaxseeds
- Hemp
- Beans
- Soy
- Oats
Different types of peptides have varying effects on the body, depending on the type of amino acids they contain. In general, scientists and fitness professionals alike are most interested in those peptides that promote anti-aging effects, and those that promote muscle growth and repair.
Collagen peptides, found in many supplements today, are known to promote skin and hair health, and stimulate the growth and development of the body’s own collagen, a natural way to combat fine lines and wrinkles. Creatine, by comparison, is known to build strength and muscle mass by working in muscle tissue to strengthen fibers, and even grow new tissue where it’s needed.
Uses Of Peptides: Why Are People Taking Them?
Several benefits have surfaced as a result of additional research on peptides and their effects on the body. Some of these benefits point to:
- Improved blood pressure – Clinical trials involving peptides derived from food sources showed a reduction in blood pressure in those who suffered from mild to moderate hypertension. This was due to a suppression of a specific enzyme that triggered an inflammatory response in the circulatory system, resulting in lower systolic pressure.
- Improved health of the microbiome – Both protein and peptides can play a critical role in developing a healthy microbiom. Our microbiome is essentially the health of our digestive system – maintaining a delicate balance of good vs. bad bacteria in the gut can significantly impact our overall health and wellness.
- Reduced inflammatory response – Proper protein synthesis is absolutely critical for overall health and wellness; it’s thought that peptides provide an enzymatic trigger for the correct processes to take place. Diseases like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and inflammatory bowel syndrome could be dramatically improved with the introduction of peptides through diet and supplementation.
- Enhanced immune function – Peptides are key players in the body’s fight against inflammation and infection. They play a critical role in improving the health and strength of the immune system, helping to keep both acute and chronic conditions at bay.
- Can help prevent age-related bone loss – Although human trials have not yet been conclusive, animal research points to a strong correlation between collagen ingestion and an increase in bone density. This evidence holds promise that peptides can help to prevent the loss of bone density that typically occurs with age.
- Improved wound healing – Collagen has long been known as a building block of healthy skin; simply improving levels of collagen within skin, hair, and nails could potentially speed wound healing and recovery time.
- Slower aging process – Who doesn’t want to look years younger and feel incredible? Peptides may be the answer to more youthful skin and beautiful, healthy hair. Collagen is present in both skin and hair cells; as peptides are increased through diet and supplementation, they go to work helping to facilitate the growth of new, healthy cells. Fine lines and wrinkles may be reduced, and your skin takes on a more youthful appearance. Combined with creatine for stronger bones and muscles, it could be possible to turn back the clock and reclaim some of that energy and vitality that you crave.

A Most Interesting Link: Peptides And The Aging Process
Just what is the link between peptides and the aging process? Aging is, essentially, the gradual inability of the body to synthesize proteins correctly; this eventually leads to the breakdown, malfunction, and death of living tissues. Various factors play a role in this gradual decline: from lifestyle factors and diet to stress and genetics; it was once thought to be an inevitable part of life.
Scientists are now discovering that these natural protein derivatives are able to facilitate healthy protein synthesis in all cells. Peptide bioregulators were first discovered and researched in the 1980s, and researchers concluded that each organ and tissue in the body uses peptides in a specific way. Even when isolated from these tissues, these peptides trigger the protein synthesis that’s most common in the organs that they’re derived from.
For example, a peptide taken from a prostate gland would regulate a prostate gland’s function, and work to repair and regenerate tissue of that kind. This is very exciting news in the medical community, as it means that it could be possible to restore and repair tissues that are stimulated correctly by peptides, rather than experiencing breakdown and degeneration of tissues that lead to aging and disease.
Peptides are also commonly used to stimulate the production of HGH, or Human Growth Hormone. This hormone circulates throughout the body in abundance when we’re younger, and declines with age; peptides are capable of pumping up the production of this youth hormone that helps to increase lean muscle mass, regulate metabolism, and lower body fat percentage.
How Should Peptides Be Used?
Peptide supplements can be classified into natural and synthetic compositions. Natural peptides, also called “cytomaxes,” are extracted from the organs and tissues of young animals. As they’re injected or ingested into the human body, they’re broken down into amino acids that match the DNA of those respective tissues or organs.
Synthesized peptides, also known as “cytogens,” have an almost immediate effect on the body. Unlike the natural peptides, these substances are comprised of single peptide molecules, rather than a chain of peptides. To get the benefits from both compositions, it’s become popular to use synthesized peptides and chase them with a course of cytomaxes for good measure.
Peptides such as Crystagen (for enhanced immune system response) and Vesugen (for cardiovascular health) are designed to repair and regenerate only those tissues that it was intended for. In the case of Crystagen, peptide molecules go to work, normalizing and restoring immune system function by restoring correct protein synthesis within immune system cells. Vesugen acts by going directly to diseased and compromised blood vessels, strengthening tissues and repairing walls, strengthening muscles, and promoting healthy circulation.
Administering Peptides
Peptides can be administered in various ways. Peptides come in powdered form, in which case they’d have to be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water and injected subcutaneously. These injections can be administered via standard insulin syringes; if you have questions about administration, talk with your medical care professionals about the proper way to self-administer a dose to avoid complications. courtesy of the crazy lifestyle of one Ben Greenfield.
Peptides can also be administered via oral capsules; it’s essential to preserve the integrity of peptides by keeping them in a cool, dark place until you are ready to administer them. Doing so will ensure that you’re getting the most benefit out of your protocol.
Powerful Peptides
These power-packed peptides are designed to rebuild and repair tissues, turn back the clock, and make you feel generally amazing:
- Epitalon – This peptide is one of few substances known to activate the telomerase response in humans. The telomere is the protective end cap on a DNA strand, and it’s responsible for protecting this precious strand against free radical damage that can lead to degeneration and disease. To administer, simply ingest a dose of 5 to 10 mg per day, once for a low dose and twice for a high dose. Repeat this cycle for 10 to 20 days once or twice a year for best results.
- Thymalin – This all-encompassing peptide stimulates the thymus gland, which is responsible for the regulation of the cardiovascular, immune, endocrine, and nervous systems, and the metabolism. It’s also very effective at promoting the body’s natural systems of detoxification. To administer, take one 10 mg dose daily for ten days, repeating the cycle only once per year.
- GHK-Cu – This peptide is known as the tissue-regenerating peptide; it’s responsible for healing wounds, improving cellular immunity, and promoting new skin and blood vessel growth. The recommended dosage for GHK-Cu is 1.5 mg per day for single doses, and it can be safely used in multiple uses up to 200 mg per day. Use this cycle for 5 to 10 days once a year for best results.

Are There Side Effects With Peptide Use?
Professor Vladimir Khavinson is a forerunner in the arena of peptide research; forty years of research and thousands of patient testimonials attest to the fact that there have been almost no harmful side effects as a result of proper administration. Peptides and amino acids are naturally occurring substances that are readily assimilated by the body, but if you wish to begin with a conservative dose to see how the body responds, this course of action is recommended for most.
The fact that there’s almost no data that points to adverse reactions to using and incorporating peptides into a wellness regime leads many to conclude that we may have just found the secret weapon against aging, illness, and degeneration – but proceeding with caution, and with the support of your doctor, is always the way to go. None of this information should be construed as medical advice.
