Is Your Microwave Oven Safe?

It’s rare to find any kitchen these days without a microwave oven. They’ve become ubiquitous in modern society since Amana introduced the first countertop unit in 1967. The cost of Amana’s Radarange that first year was $495, which translates to $3,513 in today’s dollars— pretty expensive considering you can pick up a small one nowadays for $30-$40. But the nagging question in many people’s minds is this: Are they really safe?
What are EMFs and Are They Harming Your Health?
Moving and using electricity produces electromagnetic fields (EMFs) that can range from very weak to incredibly strong. Microwave ovens occupy a part of the electromagnet spectrum shared by items that emit electromagnet radiation in the radio frequency (RF) range, including radios, televisions, radar, cell phones, WiFi networks, remote controls, and blue tooth devices. Weaker intermediate frequency (IF) EMFs are produced by computer screens, anti-theft devices, and security systems. Even weaker are the extremely low frequency (ELF) EMFs produced by the electrical supply and most of the appliances you plug into it. The aforementioned EMFs are on the non-ionizing end of the electromagnetic spectrum, meaning they aren’t strong enough to cause instant damage as do sources at the ionizing end of spectrum such as diagnostic and therapeutic radiation using x-rays, not to mention certain kinds of ultraviolet rays and some gamma rays. Radiation on the ionizing end of the spectrum can cause cellular and DNA damage such as burns, radiation sickness, cancer and genetic damage.
The radiation emitted by a microwave oven falls within the non-ionizing end of the electromagnetic spectrum, which means it doesn’t instantly break molecules up in damaging ways. Does that mean you’re safe using a microwave oven? Some people believe they are not safe, while others claim they’re fine. What should you believe?
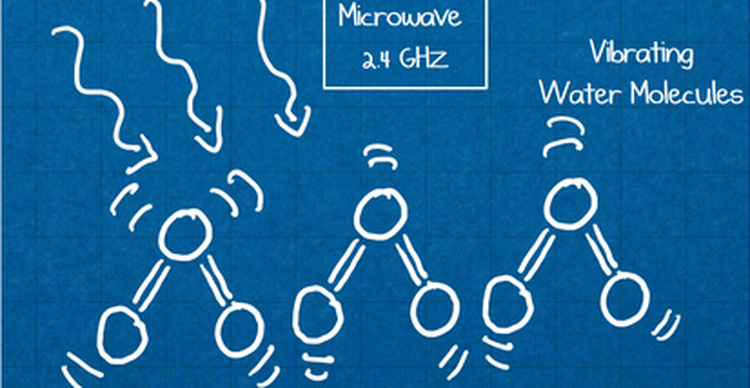
How Do Microwave Ovens Even Work?
Even though non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation doesn’t have the instantly damaging effects of ionizing radiation, it does still have an effect on things. Although it doesn’t break molecules apart, it does excite some of them. Microwave radiation is of a greater frequency than radio waves, but less than infrared radiation. The way it works is that it induces polar molecules such as water molecules (those that have oppositely charged ends) to rotate rapidly, which in turn produces heat that rubs off on nearby molecules, thereby rapidly heating food. This is what is happening inside your microwave oven in a very concentrated way.
Do Microwave Ovens Emit Radiation?
The short answer is yes, microwave ovens do emit radiation, but it’s so little that you really needn’t worry about it, unless you’re prone to pressing your face against the glass while it’s operating for hours at a time every day over the course of many years.
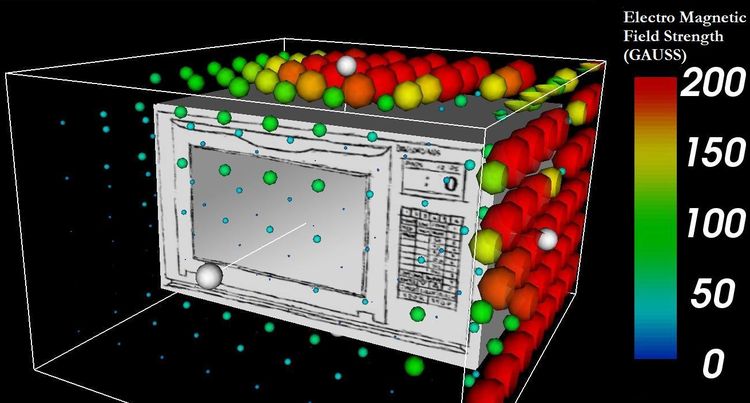
What About Standing in Front of a Microwave While it’s On?
The FDA has a limit for what microwave ovens are allowed to emit: No more than 5 milliwatts (mW) of microwave radiation per square centimeter (cm2) at distance of two inches from the microwave. Your cell phone actually emits a lot less than that; typically in the .01-.04 mW/cm2 range when making a call. However, now you have to consider how often you’re using each of these devices. Your microwave emits more radiation, but you probably use your cell phone a whole lot more than your microwave oven. Having your cell phone on your person in silent mode or talking on it a lot adds up quickly into a lot of exposure.
Even with the more substantial amount of radiation emitted from your microwave oven, all you have to do is step away from it. Twenty inches of distance drops the measured radiation to a hundredth of the amount at two inches away. If you’re going to obsess about radiation exposure, you’re probably at much greater risk from your cell phone if you talk on it a lot and carry it around with you all the time in silent mode.
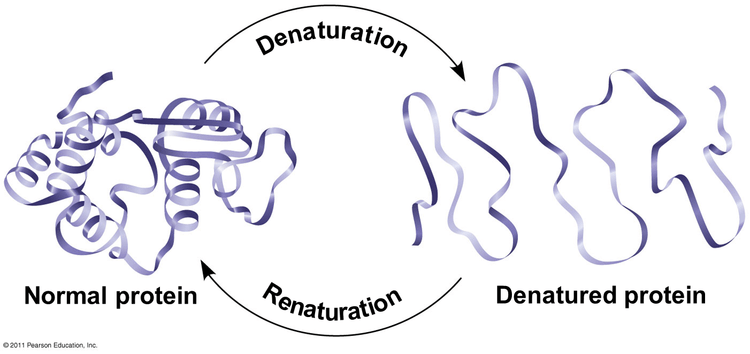
Effect of Microwave Ovens on Food
Some people go so far as to claim that microwaving food turns it into toxic sludge. That is simply not true. The anti-microwave crowd will say that it messes with the proteins of your food because it denatures them. Well, so does any form of cooking that involves high heat. When proteins are denatured, it simply means that their structure is changed— a kind of unfolding of their three-dimensional shape, nothing more. All the same amino acids are still there and bonded together.
The other thing that can denature proteins is a change in pH. This is what happens when we digest our food. In fact, proteins have to be denatured so your digestive enzymes can then break them down into individual amino acids for absorption. Cooking food jump-starts this process and makes cooked food more easily digestible than raw food. Denaturing the proteins in food is perfectly natural!
People also used to claim that microwaving food would change the amino acids from their L-form (the kind human bodies can use) into their D-form, which we can’t use and might potentially be toxic in large amounts. As it turns out, it’s true that extremely high heat is required for this change to happen, but it’s way beyond anything your microwave can do.
Then there’s the matter of nutrients. The anti-microwave crowd will say that microwaving food leaches out or destroys all the nutrients. Once again, this is largely not the case. Overcooking your food by boiling it in water removes more nutrients than most microwave cooking, which happens over much shorter periods and typically involves little water.
The effect of any kind of cooking on nutrients is all about length of time and temperature. The higher the temperature and the longer the cooking time, the more nutrients you lose. But there’s no evidence that microwave cooking is inherently worse than any other kind of cooking. The thing to remember about cooking is this: slow and low is the way to go.

Summary
To be frank, when it comes to the safety of microwave ovens, don’t believe the hype of the fear mongers. Yes, microwave ovens emit radiation, but it’s too little to worry about. You’re probably exposed to a lot more radiation from your cell phone, and with your microwave oven all you have to do is take a couple steps away from it when it’s on.
Yes, microwaving food denatures its proteins, but there’s nothing inherently wrong with that. In fact, it’s a natural part of the digestion process! And there’s no evidence that microwaving food lessens its nutritional profile any more than any other cooking method. In many cases, microwaving actually retains more nutrients than other methods because of the shorter cooking times and less water involved.
But if you’re still leery about “nuking” your food, then don’t. Use whatever cooking method you feel most comfortable with, keeping in mind that slow and low is the way to go.
