How to Test for Hidden Food Allergies or Sensitivities

If you’re experiencing a variety of health symptoms and have no known food allergies or sensitivities, you might wonder why you’d need to test yourself for them. You may believe that simply cleaning up your diet and eliminating soda, baked goods, sugar, and processed foods is enough. And while that’s certainly a good start, it’s not nearly enough to eliminate the immune and inflammatory processes that food reactions can cause.
Since eating is such an automatic process for most of us, we never stop to consider whether the symptoms we’re experiencing are related to food unless the reaction occurs while we’re actually eating or very soon thereafter.
If you have brain fog, fatigue, congestion, rashes, joint pain, or headaches, there’s a pretty good chance that your body is reacting to something you’re eating.
For many people, food is the most inflammatory substance they encounter on a daily basis. Because we eat multiple times a day, and because we’re creatures of habit, we tend to consume the same things, giving the immune system the opportunity to react.
Food sensitivities and allergies cause many symptoms, especially if you have a leaky gut. Any symptoms of inflammation or autoimmunity can point to food intolerances, so the list is vast.
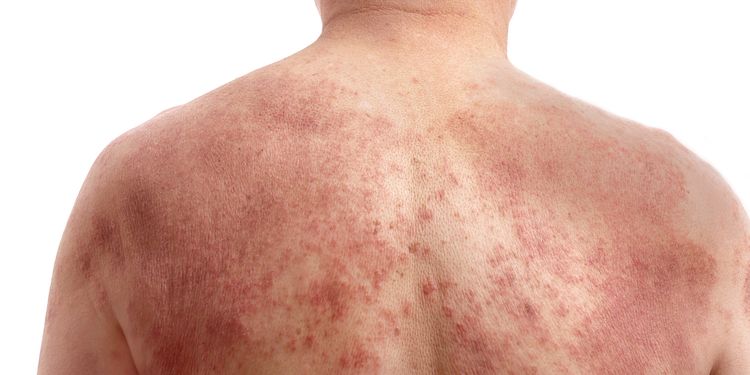
Symptoms of Food Allergies and Sensitivities
The symptoms of food intolerance can manifest quickly, as with a swollen tongue or anaphylaxis, but quite often the symptoms are delayed. This makes them hard to pick up on, as well as attribute to a certain food.
Immune/inflammation: Allergies, asthma, runny nose, post nasal drip, unresolved infections, autoimmunity, swelling, wheezing, coughing, anaphylaxis, throat closing.
Skin/hair/nails: Dermatitis, eczema, acne, rashes, scaly skin patches, hives, photosensitivity (sun sensitivity), hair loss, nail pitting, dry eyes, skin, and mouth.
Gastrointestinal: Stomach pain, GERD (acid reflux), IBS, gas, bloating, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, gastroparesis (delayed stomach emptying), canker sores.
Brain and mood: Headaches, brain fog, inability to focus or concentrate, double vision, blurred vision, poor memory, depression, anxiety, irritability, fatigue, lethargy, dementia, insomnia.
Nerves: Tingling, pins and needles, numbness, paresthesia.
Hormones: High or low blood sugar, weight gain or loss, excessive sweating.
Musculoskeletal: Joint and muscle pain, muscle weakness, fibromyalgia.
Liver: Poor detoxification, chemical sensitivity.
Cardiovascular: Low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, palpitations.

The First Food Allergy or Sensitivity Test To Perform
The first method of screening isn’t a lab test at all. It’s an elimination diet. Eliminating the most common sources of food intolerances is a great way to find out if you have an issue.
Removing gluten, dairy, corn, soy, eggs, and nuts from your diet for 4 weeks, then adding them back one single food (not food group) at a time over a period of 3 days should tell you whether your body is reacting to something.
If you have a known autoimmune condition, you may also want to include the nightshade vegetables, such as tomatoes, potatoes, sweet and hot peppers, eggplant, and spices made from these, as well as gluten cross-reactive foods like coffee, chocolate, and the gluten-free grains.
If any of the previously mentioned symptoms appear during that 72-hour window, you should avoid that food for at least 6 months to give your immune system a break and let the inflammation go down.
This method can you help you to identify the source of your food troubles, but for some, reactions can occur to even the healthiest foods, such as blueberries or spinach, especially if they have a leaky gut. To further complicate matters, not only do the foods themselves cause a response, but the additives, colorings and gum resins (binders used in gluten-free foods) do as well. This is where testing can be valuable.
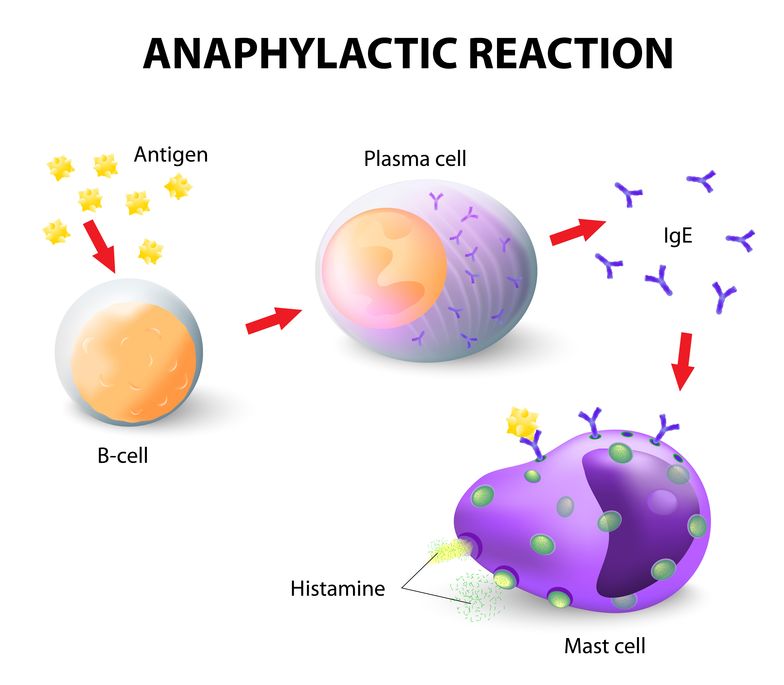
Food Allergies vs Food Sensitivities
Food allergies and sensitivities are very different issues. A food allergy occurs when the immune system identifies a food as a foreign substance and attacks it. This response occurs on a spectrum and can be anything from a swollen tongue to anaphylaxis, which is a potentially life-threatening reaction.
Food allergies are tested by measuring antibodies in the blood against particular foods. IgE and IgG are commonly measured. If you have an obvious response to a food, you can confirm it with this type of testing.
Food sensitivities are the more common and elusive form of food intolerance. They’re more vague than allergies and are considered to be any toxic or inflammatory response to food. Quite often they’re mediated by a lack of enzymes, stomach acid, and/or a leaky gut. Celiac disease is a perfect example, where a severe intolerance to gluten causes the destruction of the surface of the small intestine.
Testing for food sensitivities offers a variety of options; antibody and mediator release testing (MRT) are two of the better ones available. No matter what test you choose, be aware that if you have a leaky gut, there’s a good chance you’ll be reacting to many of the foods you eat.

Food Allergy and Sensitivity Tests
There are several types of testing available for identifying food allergies and sensitivities. IgE testing represents the true food allergy test. IgG testing can also identify allergies, but more commonly, it shows delayed sensitivity reactions. The rest of the testing options are for intolerances or sensitivities only.
- IgE antibody test
- IgG and IgA antibody test
- Gluten and gluten cross-reactivity tests
- MRT test
IgE Antibody Testing for Food Allergies
Antibodies are produced when your body mounts an immune attack on a substance it has identified as foreign, which in this case is food. It creates antibodies against specific proteins (antigens) in that food. Antibody tests measure your body’s immune response to a particular substance or organism.
There are several categories of antibodies. IgE antibodies are created when your body has a true allergic response to a substance, which is why traditional food allergy testing analyzes antibody levels in the blood. An IgE allergy is considered a fixed allergy in that it will almost always provoke an immune response when the food is consumed. This type of food allergy elicits an immediate response.
This test can be completed by traditional labs such as LabCorp or Quest, as well as the specialty lab companies Alletess Medical Laboratory and Great Plains Laboratory. IgE testing can easily be ordered online through Direct Labs.
IgG and IgA Antibody Testing for Food Allergies and Sensitivities
In spite of having an allergy, you can still yield a negative IgE test result. This is why it’s important to test IgG levels as well. IgG antibodies measure a delayed hypersensitivity reaction, which can take up to 72 hours to occur. These are the more difficult reactions to link to a particular food, so testing can be helpful here. IgG antibodies are the most prevalent antibodies in systemic circulation and are the most common form of immune-mediated food responses.
While some IgG responses represent true allergies, most are hypersensitivities or intolerances. Similarly, IgA antibodies also represent delayed hypersensitivities. They can take many hours or days to occur and operate in a low-and-slow manner.
Traditional labs such as LabCorp or Quest will offer this test. Genova Diagnostics offers an IgG test. Alletess Medical Laboratory offers stand-alone IgG testing, combined IgG and IgE testing, and IgA testing. Cyrex Laboratories offers the Array 10: Multiple Food Reactivity Screen that measures IgG and IgA levels. The Array 10 tests raw and cooked foods, additives, gum resins, and brewed beverages.
All of these IgG and IgA tests can be ordered online through Direct Labs.
Gluten and Gluten Cross-Reactivity Tests
If you suspect that you’re sensitive to gluten, or even have full-blown celiac disease, testing is an important piece of the puzzle. Gluten testing involves analyzing the IgG and IgA response to various components of the gluten molecule, including several gliadins, glutenins, gluteomorphins (made during the digestion of gliadin), and the intestinal enzyme transglutaminase. It’s important to note that you must consume gluten for this test to be as accurate as possible.
Once you confirm gluten intolerance or celiac disease, completing gluten cross-reactivity testing is helpful, since these foods elicit the same response from the immune system as gluten does. This means that they contain similar protein sequences as the gluten molecule (molecular mimicry). Milk, whey, chocolate, coffee, soy, potatoes, corn, eggs, and most gluten-free grains (including rice) are considered cross-reactive.
Conventional lab companies offer gluten testing and the Array 4: Gluten Associated Cross-Reactive Foods test. This test can be ordered online through Direct Labs.
Mediator Response Test (MRT)
The MRT utilizes different technology than antibody testing. It quantifies the inflammatory response to specific foods and additives. Mediator release refers to the inflammatory chemicals that are liberated from your cells in response to a sensitizing food.
Instead of measuring antibody production, this test measures your white blood cells’ chemical response to a food. It gauges the cells’ change in volume, which comes from the release of inflammatory chemicals such as histamine and cytokines. A non-reactive food will produce no change, while a reactive food will produce an increase or decrease in cell volume.
This is a blood test and is only offered by Oxford BioMedical Technologies.
The Bottom Line on Food Allergy and Sensitivity Tests
Start with the basics and conduct an elimination diet. That alone will give you new information to work with. From there, spend money only on the testing that could reveal new information that would alter your approach to food. If you’re already 100% gluten-free and are avoiding all cross-reactive foods as well, then gluten testing would be a waste of time and money.
So be smart and be proactive. Discovering hidden food allergies or sensitivities could make a huge difference in your day to day health.
